Introduction
In modern industries, waste gas treatment equipment plays a vital role in ensuring clean air emissions. Along with systems such as RTO (Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer), CO (Catalytic Oxidizer), RCO (Regenerative Catalytic Oxidizer), and zeolite rotor concentrators, different filtration grades are essential for removing harmful particles. Below we introduce the five common filtration grades and their characteristics in air pollution control equipment.
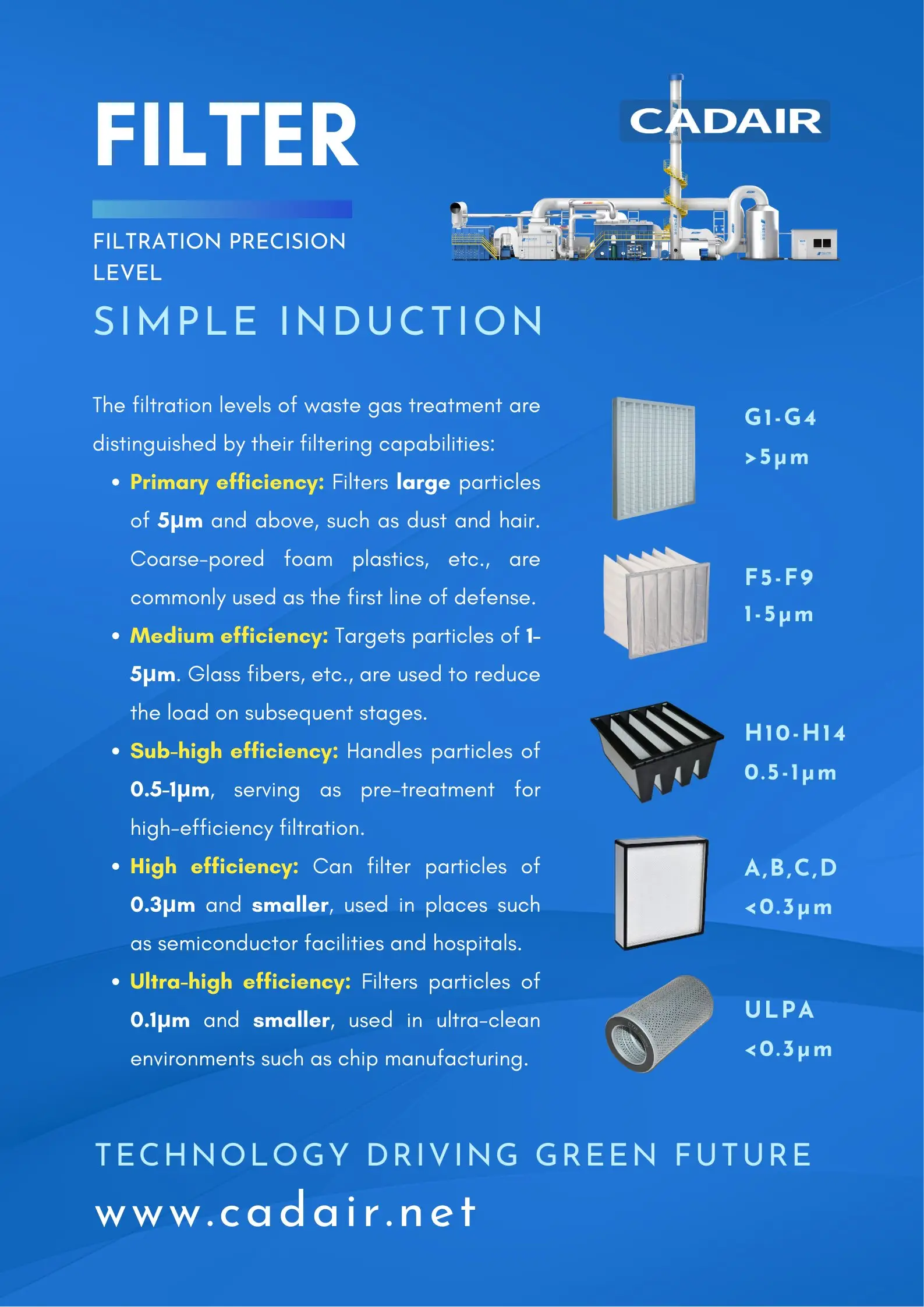
1. Primary Filtration
Primary filtration targets large-sized particles such as dust, hair, fibers, and debris above 5μm.
- Materials: coarse-pore foam plastic, metal wire mesh, synthetic fibers
- Advantages: simple structure, low cost
- Function: protects downstream pollution control equipment from abrasion and blockage
👉 Typically installed at the entrance of ventilation systems, primary filters act as the first line of defense in waste gas treatment equipment.
2. Medium-Efficiency Filtration
Medium-efficiency filters capture particles between 1–5μm.
- Materials: glass fibers, synthetic fibers, non-woven fabrics
- Function: reduces the load on downstream high-efficiency filters, extends service life
- Applications: intermediate stage between primary and high-efficiency filtration; sometimes used alone in less strict conditions
👉 In many industrial air pollution control equipment setups, medium-efficiency filters ensure stable VOC treatment performance.
3. Sub-High-Efficiency Filtration
Sub-high-efficiency filtration handles particles between 0.5–1μm.
- Materials: finer fiber materials
- Advantages: higher efficiency than medium filters
- Applications: pre-filtration in high-demand industries (electronics, pharmaceutical cleanrooms)
👉 This stage improves the overall efficiency of environmental protection equipment, especially in industries with strict emission requirements.
4. High-Efficiency Filtration (HEPA)
High-efficiency filtration removes particles of 0.3μm and smaller, with efficiency up to 99.97% (HEPA standard).
- Materials: ultra-fine glass fiber paper, advanced synthetic fibers
- Applications: semiconductor exhaust, biological laboratories, hospital operating rooms
- Function: ensures discharged waste gas meets strict air quality standards
👉 Often combined with thermal oxidizers or catalytic oxidizers, HEPA filters guarantee high-quality emission control.
5. Ultra-High-Efficiency Filtration (ULPA)
Ultra-high-efficiency filters (ULPA) remove particles of 0.1μm and smaller, with efficiency over 99.999%.
- Applications: high-end chip manufacturing, ultra-clean environments
- Role: essential for industries requiring the highest level of environmental control
👉 In advanced RCO and CO systems, ULPA filtration ensures compliance with global emission standards.
Conclusion
From primary to ultra-high efficiency filtration, every grade contributes to comprehensive VOC treatment in industrial emissions. Combined with advanced pollution control equipment such as RTO, CO, RCO, thermal oxidizers, and zeolite rotors, these filtration systems form the backbone of CADAIR’s solutions.
👉 Discover more about our Environmental Protection Equipment and explore how CADAIR can provide customized waste gas treatment solutions for your industry.